Support in Insurance Claim
No-Cost EMI
Without Admission
Short Hospital Stay
4.9 Rating on Google
Benefits

Minimally Invasive

Reduces Stroke Risk

Faster Recovery

Preserves Blood Flow
To Book An Appoinment
Understanding Carotid Arteries and Stroke
The carotid arteries are two blood vessels that are located on either side of the neck. They carry the oxygen-rich blood of your heart directly to your brain, vital to keep the brain in good health and alert. If these arteries narrow due to plaque accumulation (a process referred to as atherosclerosis) blood flow to the brain could be reduced or stopped for a short time, resulting in stroke. A stroke happens because the brain has been depleted of oxygen, which causes brain cells to cease to function within minutes. the reduced blood flow could cause mini-strokes, or transient Ischemic attacks (TIAs) which are warning signs that indicate a stroke that could be imminently major.
To prevent this, carotid angioplasty with stent is often performed. This procedure is minimally invasive and makes use of a small balloon to expand the artery and an inserted stent to maintain it open, while restoring normal blood flow into the brain. This new treatment can reduce stroke risk, eliminate open surgery and encourages speedier recovery.
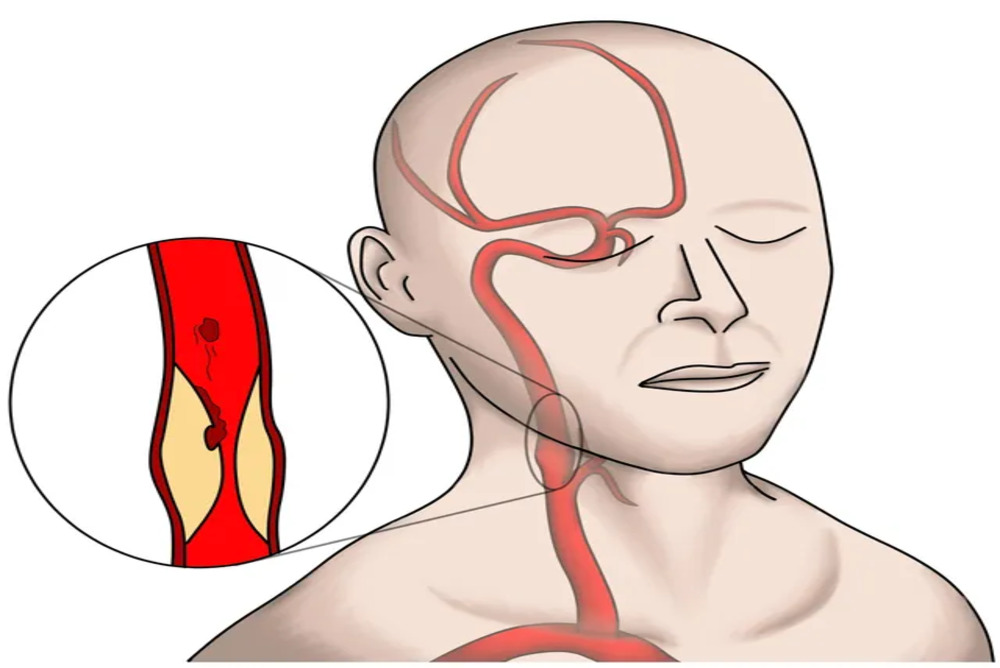
What Is Carotid Artery Stenosis?
Carotid artery stenosis is the medical term that describes the carotid arteries that narrow, typically caused by atherosclerosis, which refers to the build-up of fat (plaque) inside the walls of arterial vessels. As the years progress, plaque could develop or break, limiting circulation, increasing the chance of blood clots that could be carried towards the brain which can lead to stroke.
Risk factors that may cause carotid artery stenosis:
- The cholesterol levels are very high.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Insulin resistance, also known as diabetes
- Smoking cigarettes and smoking tobacco
- A poor diet and a sedentary lifestyle
- Family history and ageing are the most common causes of vascular diseases
If not treated, Carotid stenosis could develop in a silent manner until it leads to grave complications like strokes, TIAs, or even a stroke. The early detection and treatment are essential to avoid the development of permanent neurodegenerative damage.
From a medical coding standpoint doctors use carotid artery disease ICD 10 classifications to record and track the condition in a precise manner making sure that the appropriate treatment is provided, as well as insurance documents.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Stenosis
In a majority of instances, carotid arterial narrowing does not manifest until the arteries become significantly narrowed. However, certain symptoms could suggest a decrease in the flow of blood into the brain. Patients should look out for signs of:
- Numbness or weakness that suddenly occurs in either side of your arm, face or leg
- Trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Loss of vision or blurred vision in both eyes or one eye
- A sudden dizziness or loss of coordination
- Headache is severe with no root
- Mini-strokes or transient Ischemic attacks (TIAs)
These could be indications that the brain is not getting sufficient oxygen. Anyone who experiences these symptoms must seek medical attention immediately. After a thorough examination those with significant narrowing could be candidates for carotid artery stenting which could increase blood flow and to prevent major strokes. At IRFacilities the doctor Dr. Sandeep Sharma uses advanced diagnostic tools to determine the degree of obstruction and recommend the most appropriate treatment.
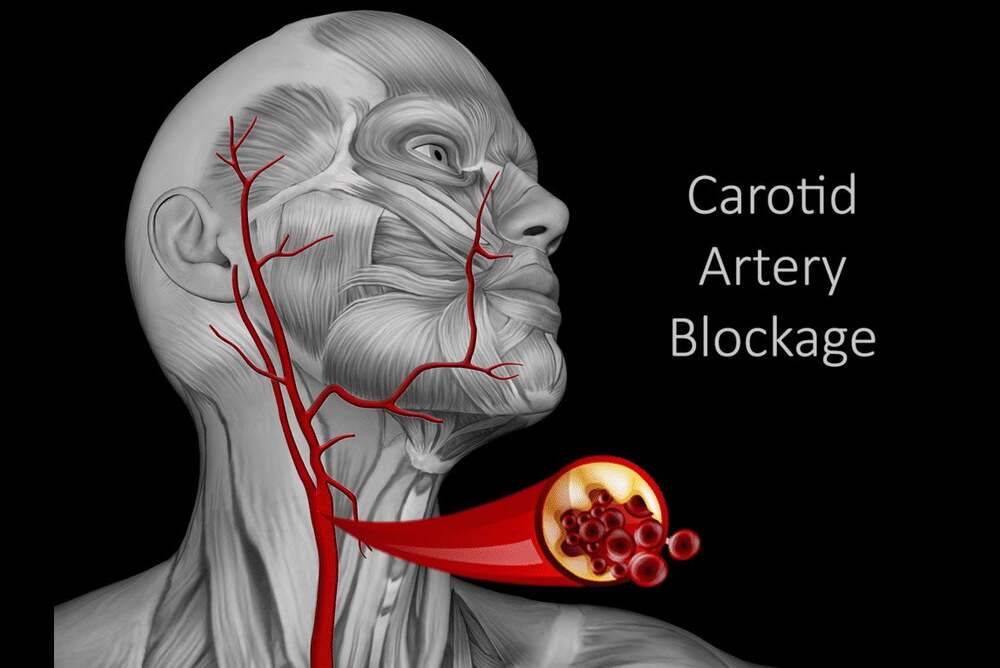
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery Stenosis
A successful treatment plan is based on an accurate diagnosis. Dr Sandeep Sharma conducts a number of minimally-invasive and noninvasive tests to determine the severity and determine whether the carotid or stent procedures are necessary.
- Carotid Ultrasound (Doppler): Sound waves are used to assess blood flow and identify the narrowing.
- CT Angiography (CTA) uses the use of X-rays with contrast dye to produce precise images of arteries.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) provides 3D images of blood vessels with magnetic fields.
- Cerebral Angiogram is an image-based test that uses a catheter to allow accurate visualisation of carotid arteries.
The imaging methods allow staff at IRFacilities to assess the severity of stenosis and then design the most appropriate treatment strategy, surgery, medication management, or carotid angioplasty using the placement of stents.
Treatment Options for Carotid Artery Stenosis
The most appropriate treatment for carotid artery diseases is based on the extent of the blockage, the severity of your symptoms and general health. At IRFacilities Sandeep Sharma, offers a variety of options for patients with advanced or early stage disease, such as:
Carotid Artery Stenting (Minimally Invasive Treatment):
Carotid artery stenting is usually the first choice for patients with a higher risk of surgery. In this carotid angioplasty Stent procedure, a tiny catheter is placed into an arterial (usually located in the lower groin) and then positioned at the location of obstruction. A balloon is inflated in order to expand the artery, and then a stent is inserted for it to stay open. This improves blood flow, decreases the risk of stroke and allows for quicker recovery than open surgery.
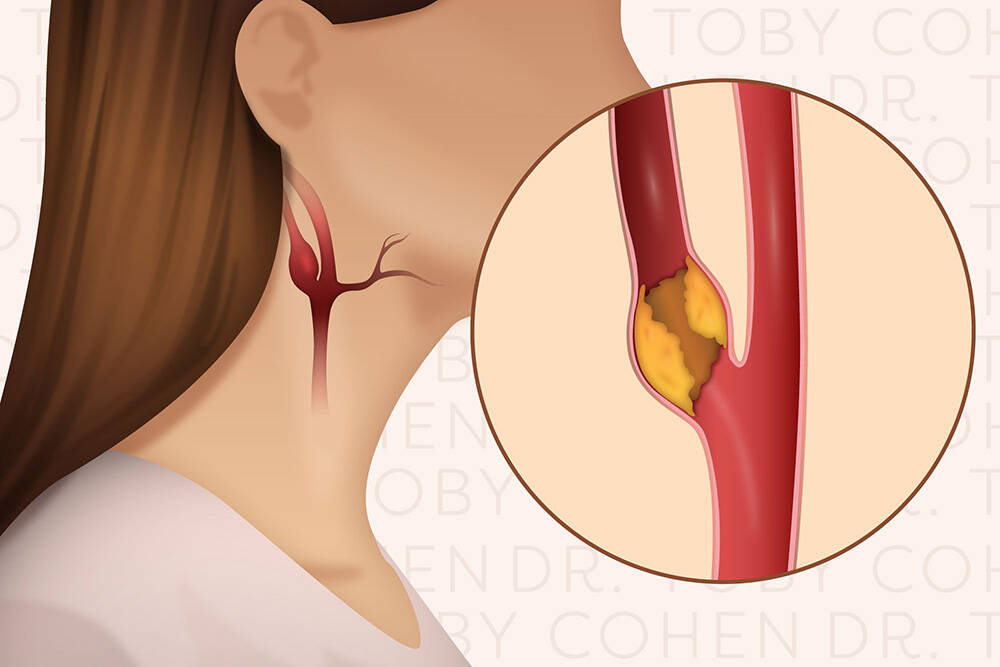

Recovery and Aftercare
The healing process following carotid arterial stenting procedure is usually faster than traditional surgical. The majority of patients remain in hospital for about 1-2 days to monitor. Following the discharge, patients are instructed to take the prescribed medication that include an antiplatelet treatment (such as clopidogrel or aspirin) to stop the formation of clots within the stent.
Long-term care includes:
- Follow-up visits to check on the stent and ultrasound scans to check the stent.
- Healthy cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
- Eating a balanced, low-fat diet.
- Engaging in light physical activities according to the guidelines of your physician.
- Beware of smoking and heavy alcohol consumption.